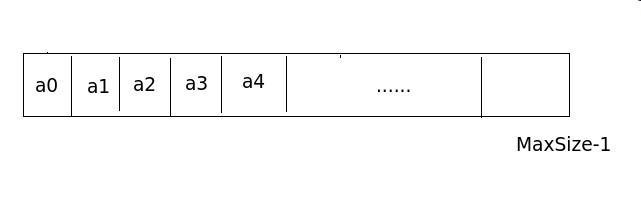
顺序表采用数组实现,并且通过继承AbstractList类,下图为顺序表的存储结构图:
具体代码如下:【详见SequenceList.java】1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76package datastructure.linear.sequence;
import datastructure.exception.StructureException;
import datastructure.linear.AbstractList;
public class SequenceList<T> extends AbstractList<T>{
/**
* 该顺序表的默认容量为10
*/
private final static int defaultCapacity = 10;
/**
* 实现顺序表的数组
*/
private Object[] arrs;
/**
* 实例化顺序表,使用默认的容量大小,为10
*/
public SequenceList() {
this(defaultCapacity);
}
/**
* 实例化顺序表, 指定顺序表的容量
* @param capacity
*/
public SequenceList(int capacity) {
arrs = new Object[capacity];
size = 0;
}
public void insert(int index, T t) throws StructureException {
if(arrs.length <= size) {
throw new StructureException("顺序表的容量已满");
}
if(index < 0 || index > size) {
throw new StructureException("参数异常!不能小于0或者大于当前长度");
}
// 插入前先后移之后的元素
for(int i = size ; i > index ; i--) {
arrs[i] = arrs[i-1];
}
arrs[index] = t;
size ++;
}
public void delete(int index) throws StructureException{
if(isEmpty()) {
throw new StructureException("该顺序表为空!不存在任何元素");
}
if(index < 0 || index >size - 1) {
throw new StructureException("参数异常!不能小于0或者大于顺序表的容量");
}
for(int i = index+1 ; i < size ; i++ ) {
arrs[i-1] = arrs[i];
}
arrs[size -1] = null;
size--;
}
("unchecked")
public T get(int index) throws StructureException {
if(isEmpty()) {
throw new StructureException("该顺序表为空!不存在任何元素");
}
if(index < 0 || index >arrs.length) {
throw new StructureException("参数异常!不能小于0或者大于顺序表的容量");
}
return (T) arrs[index];
}
}
顺序表上的插入和删除是顺序表中时间复杂度最高的成员函数。在顺序表中插入一个数据元素时,算法中时间复杂度最高的部分是循环移动数据元素。循环移动数据元素的效率与插入数据元素的位置pos有关,最坏情况是pos=0,需移动size个数据元素;最好情况是pos=size,需移动0个元素。
顺序表的时间复杂度:顺序表中的其余操作都是与数据元素个数n无关,因此,在顺序表中插入和删除一个数据元素的时间复杂度为O(n),其余操作的时间复杂度为O(1).
顺序表的主要优点:算法简单,空间单元利用效率高;主要缺点是需要预先确定数据元素的最大个数,并且插入和删除操作时需要移动较多的数据元素。
测试类:代码如下:
1 | package datastructure.linear.sequence; |